You know what a lullaby is – a song you sing to a baby that won’t sleep (hello to my nephew). ‘Lullaby’ comes from the Middle English phrase ‘lullen’, which means ‘to lull’, and ‘by’ which means, well, ‘by’ or ‘near’. So it literally translates as ‘to lull near’. We’ve been using the word ‘lullaby’ in English since at least the 16th century.
So far, so straightforward. But, there’s another, more sinister explanation. Before I get into it, I should preface this by saying this is ‘folk etymology’ which is when we change or reinterpret the origin of a word over time, usually due to a popular or widely held (wrong) belief about its meaning (see ‘penthouse’ for an example). So everything after this point is probably bollocks. But let’s just go with it, because it’s much more interesting.
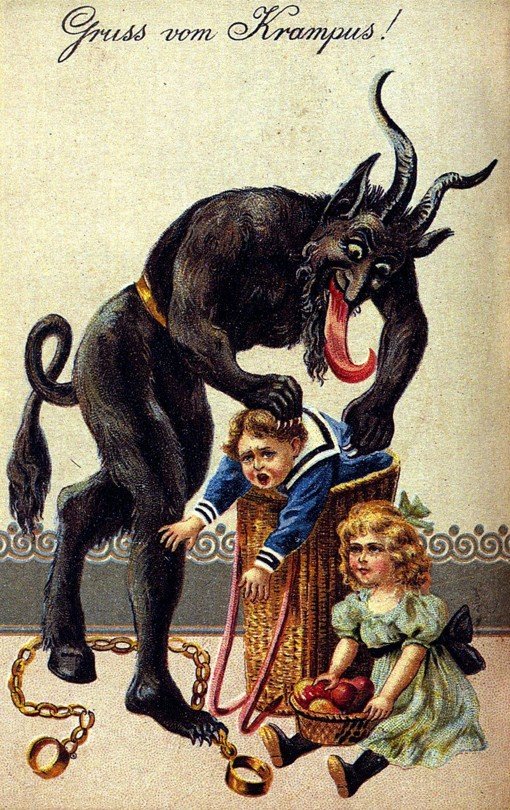
Lilith and snake pal (not the name of the painting) by John Collier
In this explanation, the word ‘lullaby’ comes from ‘Lilith abi’ which means ‘Lilith, begone’ in Hebrew. In some Jewish mythology, Lilith was the first wife of Adam, before Eve (PLOT TWIST). Unlike Eve, who was made from Adam’s rib, Lilith was created from the same clay as he was, which made them equal. Because of this she got a bit uppity – literally – and refused to lie underneath him when they were getting jiggy with it, or have his children. You go, girl.
Because of all this bloody feminism (I bet she wanted equal pay and dresses with pockets too), Lilith was either banished from the Garden of Eden or left of her own accord (I hope it was the second one). In the wilderness around the garden she became a demon who preyed on newborn infants and seduced men in their sleep (using reverse cowgirl, presumably – no missionary for our Lilith). She’s often shown as having wings, or as a snake.
Lilith appears in various Jewish texts, including the Talmud and the Zohar. And depending on who you talk to she’s either a symbol of female empowerment and resistance against the patriarchy, or a dangerous and evil woman who threatens the very order of creation. I think you can probably guess which side I come down on.
Anyway, back to lullabies. For whatever reason, Lilith has got a reputation for stealing babies. One belief is that this is because she was jealous of the attention Adam and Eve gave their children, while another says she could only have demon babies, so she stole human ones to make up for it. Either way, singing ‘Lilith abi’, or a lullaby, was a way to ward off Lilith and protect your babbie from her evil/feminist clutches.
I told you it was better than the real answer.